- Your cart is empty
- Continue Shopping
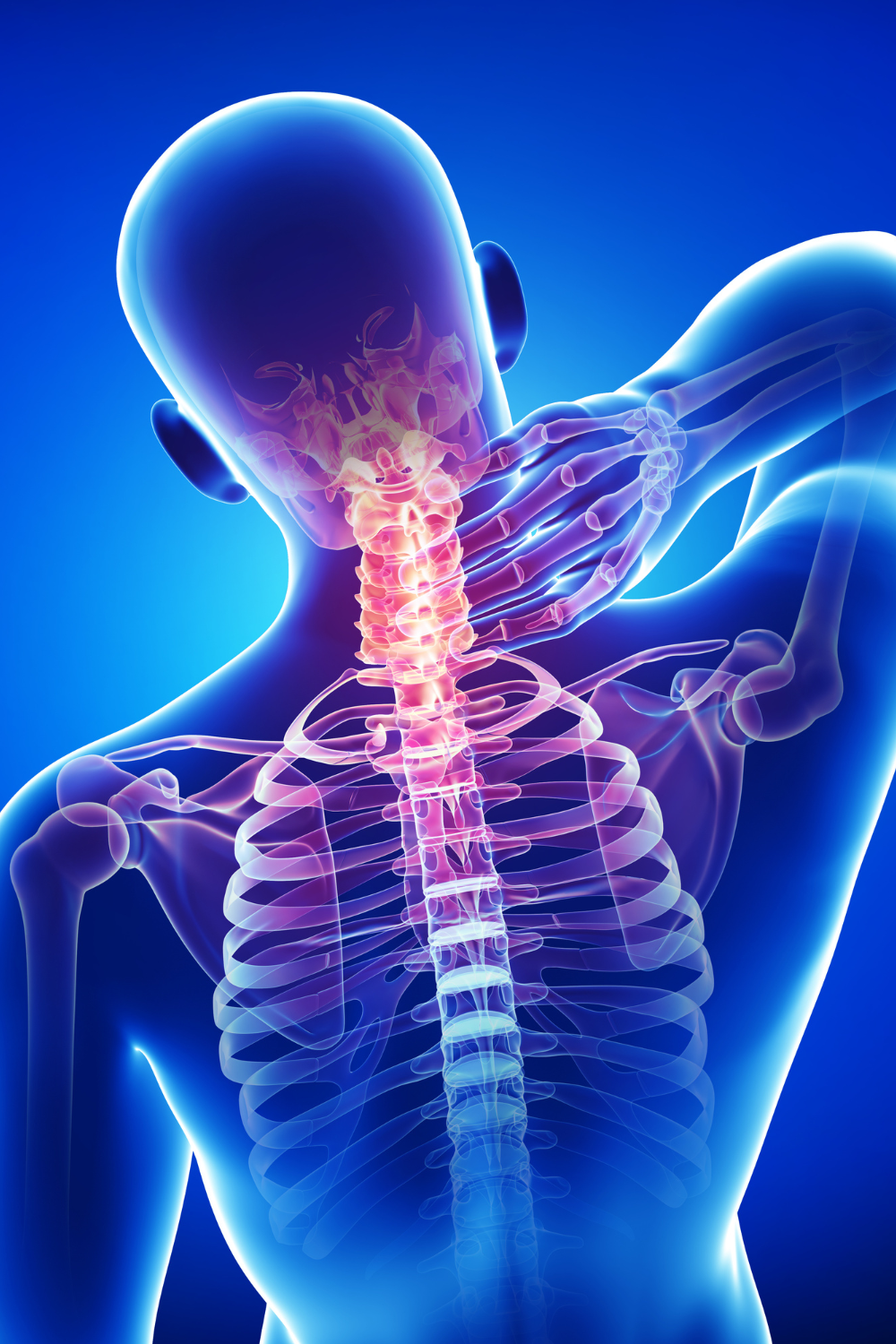
Head and Neck Cancer
Head and Neck Cancer
A Complete Guide by Medlama
A Complex Disease That Demands Compassionate, Coordinated Care
Head and neck cancer is not just a medical condition — it is a life-altering diagnosis that affects essential functions like speaking, swallowing, breathing, and appearance. These cancers can arise in the mouth, throat, voice box, nasal cavity, sinuses, or salivary glands, and are often linked to tobacco use, alcohol consumption, or human papillomavirus (HPV) infection.
While early symptoms may seem minor — such as a sore throat or a persistent ulcer — timely detection and the right treatment can greatly improve recovery and quality of life.
At Medlama, we understand that head and neck cancers require more than just treatment — they need a multidisciplinary approach that includes oncologists, ENT specialists, nutritionists, speech therapists, and emotional support teams.
What Increases the Chances of Head and Neck Cancer
Understanding the risk factors associated with head and neck cancer is essential for prevention, early detection, and making proactive health choices. While having one or more of these risk factors does not guarantee that you will develop the disease, it does increase your overall risk. Awareness empowers individuals to adopt healthier lifestyles, avoid high-risk behaviors, and seek early evaluation when symptoms arise.
01. Tobacco Use
Smoking is the most significant risk factor for head and neck cancers, including those of the mouth, throat, voice box (larynx), and esophagus. Cigarettes, cigars, pipes, and especially smokeless tobacco (such as gutkha, paan, or chewing tobacco) contain carcinogens that damage the cells in the mucosal lining of the head and neck region. Even secondhand smoke exposure may contribute to risk.
02. Alcohol Consumption
Excessive alcohol intake — especially when combined with tobacco use — dramatically increases the risk of head and neck cancers. Alcohol irritates the lining of the mouth and throat, making it more susceptible to cancer-causing agents. Long-term, heavy drinking is a major contributor, particularly for cancers of the oral cavity, pharynx, and larynx.
03. Human Papillomavirus (HPV) Infection
In recent years, HPV (especially type 16) has emerged as a leading cause of oropharyngeal cancers (cancers of the tonsils and base of the tongue). HPV-positive cancers often occur in younger individuals and are typically not linked to tobacco or alcohol use. Fortunately, HPV-related head and neck cancers tend to respond better to treatment.
04. Poor Oral Hygiene and Dental Health
Chronic dental problems, gum disease, and poor oral hygiene have been associated with an increased risk of oral cancers. Poorly fitting dentures, broken teeth, or sharp fillings that cause constant irritation or injury to the inner cheeks or tongue may also increase the chance of cancerous changes over time.
05. Occupational Exposure
Long-term exposure to wood dust, asbestos, nickel, formaldehyde, paint fumes, and other industrial chemicals increases the risk of cancers in the nasal cavity, sinuses, and larynx. These risks are higher in workers in construction, furniture manufacturing, textile, and metal industries.
06. Diet and Nutritional Deficiencies
A low intake of fruits and vegetables, which are rich in antioxidants and vitamins, has been linked to a higher risk of head and neck cancers. Deficiencies in vitamin A, C, and folate may reduce the body’s ability to repair damaged cells, contributing to cancer development over time.
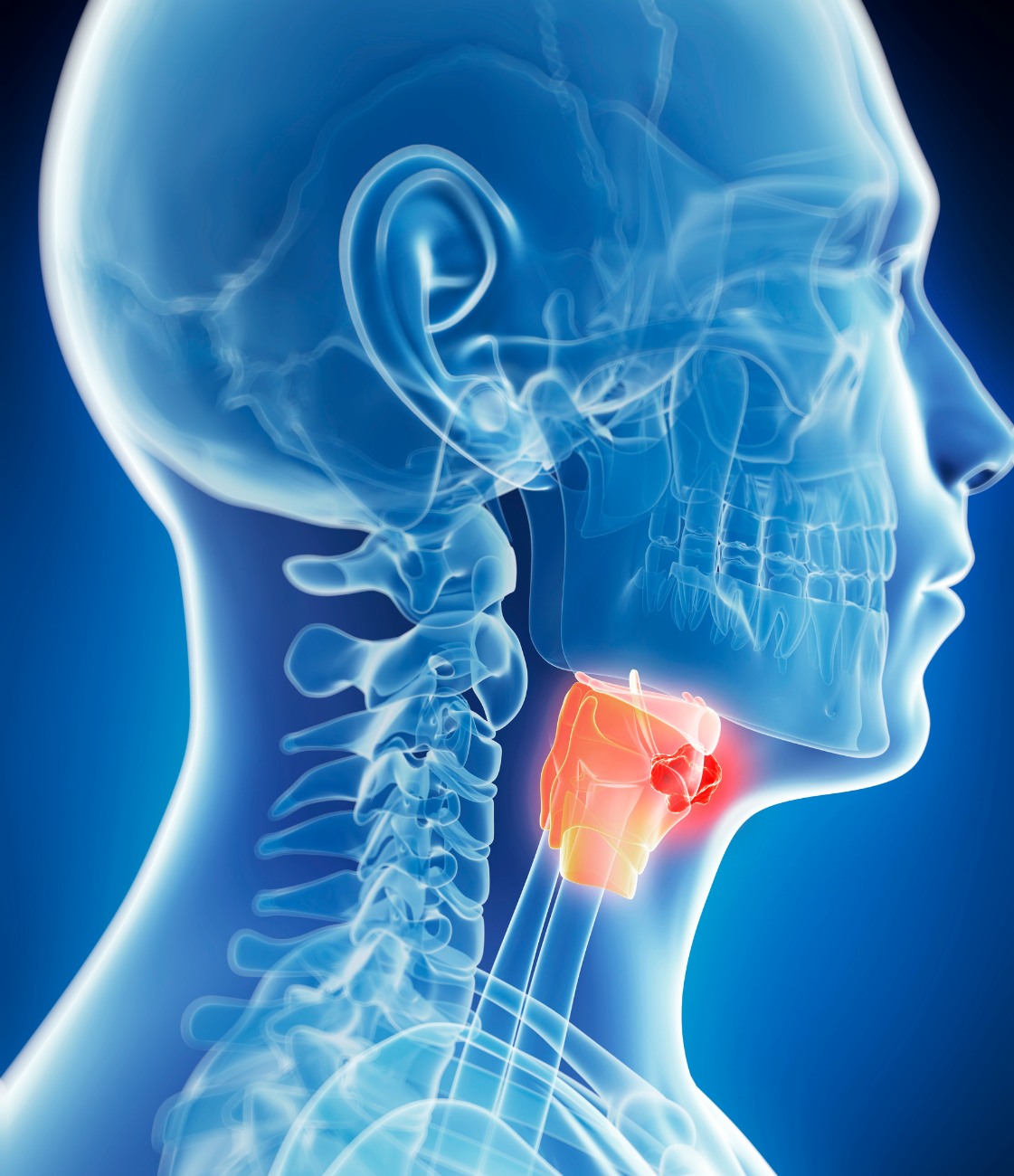
Early Awareness
What is Head and Neck Cancer?
Head and neck cancer refers to a group of biologically similar cancers that originate in the mouth, throat (pharynx), voice box (larynx), nasal cavity, sinuses, and salivary glands. These cancers typically begin in the squamous cells that line the moist surfaces of these areas and can grow aggressively if not detected early.
Many head and neck cancers go unnoticed in their early stages due to mild or non-specific symptoms such as a sore throat, hoarseness, or mouth sores. That’s why early awareness, routine screenings, and understanding the risk factors — like tobacco, alcohol, and HPV infection — are essential for timely diagnosis and better outcomes.
- Oral Cavity Cancer
- Oropharyngeal Cancer
- Laryngeal Cancer
- Nasopharyngeal Cancer
Each type of head and neck cancer presents with unique challenges and requires a tailored treatment approach.

Hidden Warnings
Signs and Symptoms of Head and Neck Cancer
Yes. Hoarseness, voice changes, or difficulty swallowing (dysphagia) are common symptoms, particularly in cancers of the larynx or throat. A feeling of something "stuck" in the throat or pain while swallowing may also occur.
A lump in the neck, jaw, or inside the mouth that doesn’t go away could be a swollen lymph node or a tumor. Swelling in the face, jaw stiffness, or an asymmetrical facial appearance may also be warning signs.
Yes. Ear pain without ear infection, numbness in the face, loose teeth, difficulty moving the tongue, or unexplained bleeding in the mouth or nose can all indicate deeper issues that should be checked immediately.
Not necessarily. Many symptoms can be caused by non-cancerous conditions like infections or minor injuries. However, any persistent or unexplained symptom lasting more than two weeks should be evaluated by a healthcare professional, especially in individuals with risk factors such as tobacco or alcohol use.
Welcome to Medlama — a holistic healing initiative under Narang Biotec — designed to support your emotional and mental wellbeing alongside medical treatment.
At Medlama, we believe that healing is not just physical — it’s also emotional, spiritual, and mental. Our aim is simple: to create a safe, empowering space where we can come together to beat cancer with strength, positivity, and support — beyond medicine.
Useful Links
Address
- 3966, 2nd Floor, Roshanara Rd, Arya Pura, Sabzi Mandi Old, New Delhi, Delhi 110007
- +91-9205022032
- contact@medlama.com
